In the history of GPU development, it's impossible to overlook NVIDIA, a company that has become the undisputed leader in the GPU industry. NVIDIA's dominance stems from its powerful GPU computing capabilities, its CUDA ecosystem, and its high-speed interconnect technology. These three pillars have not only redefined graphics processing technology but have also built a formidable moat around the company.
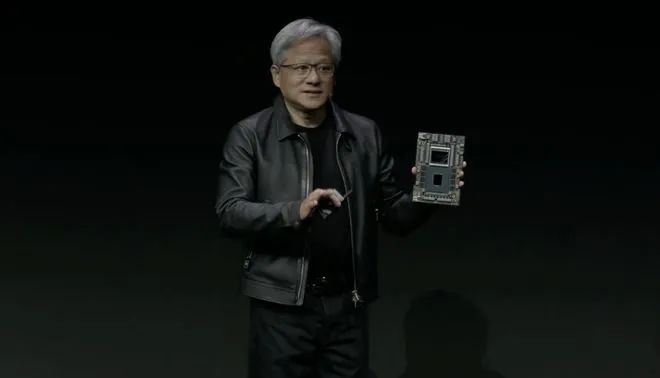
With the explosion of large AI models, GPUs have become the hottest commodity in the tech world. However, the expanding U.S. chip bans have made the already uncertain future of China’s semiconductor market even more challenging. In this difficult scenario, how can China's semiconductor companies scale the mountain that is NVIDIA and find a path forward? This is the question that every player in the industry must grapple with.
As the West tightens its technological grip, China’s AI chip industry is seeing a surge of competition. The domestic GPU market is rife with innovation and, at times, chaos. Terms like GPGPU, general-purpose GPUs, full-function GPUs, graphic GPUs, and rendering GPUs are being used in a variety of ways, adding to the confusion.

Currently, domestic GPUs in China can be broadly categorized into three functional types: AI, HPC, and rendering. AI GPUs are similar to NVIDIA's recent deep learning accelerators. HPC GPUs are used in supercomputers, supporting double-precision floating-point operations for scientific computations. Rendering GPUs handle traditional tasks like gaming, desktop graphics, and other visual applications.
Chinese GPU manufacturers can also be categorized into three main types:
So, how can these domestic players catch up? Is there still a significant gap between Chinese GPUs and NVIDIA’s offerings? And where exactly are the challenges in creating a viable alternative to NVIDIA’s dominance?
Firstly, evaluating any GPU's performance without considering the specific demands of the application is misleading. Floating-point performance, which measures how well a GPU handles floating-point calculations, is a critical benchmark, often focusing on single-precision and double-precision capabilities.
Single-precision and double-precision refer to the storage method and accuracy of floating-point numbers in computing. Single-precision typically uses 32 bits (4 bytes) to store a number, while double-precision uses 64 bits (8 bytes), allowing for a wider range and higher accuracy in calculations. NVIDIA's A100 GPU excels in both single and double-precision, making it ideal for training large AI models that require high precision and speed. In contrast, many current Chinese GPUs primarily support single-precision, limiting their effectiveness in such demanding applications.
Secondly, there’s the issue of the software ecosystem. A GPU’s hardware is only part of the equation; it must also be supported by a robust ecosystem of tools, including hardware systems, toolchains, and compilers. Without this support, a GPU might perform well in one scenario but fail to deliver in another. NVIDIA's CUDA platform has become the global standard for AI infrastructure, with most AI frameworks, libraries, and tools built around it. In comparison, the ecosystem for domestic GPUs in China is still in its infancy, making it harder for developers to create, debug, and optimize GPU programs.
Moreover, NVIDIA continues to reduce costs for users. While its cards are expensive and in high demand, the efficiency gains during large-scale model training often justify the price. For example, NVIDIA’s Blackwell architecture, with its GB100 chips, reduces costs and energy consumption to 1/25th of previous models, while delivering seven times the performance of the H100 in certain benchmarks. NVIDIA’s CEO Jensen Huang famously said, “The more you buy, the more you save,” which, in some contexts, holds true.

Gooxi, with its 16 years of experience in the server industry, is a provider of essential computing infrastructure in the AI supply chain. To meet the needs of customers transitioning to smarter technologies, Gooxi has developed a solid foundation for AI computing and offers AI privatization solutions. Additionally, Gooxi has created differentiated market capabilities through deep ecosystem integration and collaboration with multiple resources. Currently, Gooxi’s AI servers are compatible with most domestic GPU cards and can be customized to meet specific customer requirements, helping to accelerate the realization of self-sufficient computing resources in China.
Surpassing NVIDIA in the short term is almost an impossible task. However, even the mightiest of giants have their vulnerabilities, and NVIDIA is not without its challenges—from tech giants encircling it to lawsuits alleging monopolistic practices. With strong government support, China’s self-reliant GPU development path is long and arduous, but it’s also filled with opportunities. The door to domestic GPU development is slowly but surely opening.
Related recommendations
Learn more news
Leading Provider of Server Solutions


YouTube
